Your Reverse Osmosis (RO) system could waste water due to how it operates. RO systems use semipermeable membranes to filter contaminants out of your drinking water supply; once passing through this membrane, contaminants are caught and flushed away with wastewater from this process – known as waste water.
Waste water doesn’t go to waste simply because it goes unused; rather, its purpose lies in helping maintain and prevent damage to an RO membrane filtering device. Wastewater helps carry away contaminants found within it to help ensure continued filtering performance from this membrane filter system.
Traditional RO systems typically had a waste water ratio of 4:1; meaning for every gallon of clean water lost, between 3-25 may be wasted as waste. Thanks to modern advancements, more efficient designs now include waste water ratios as low as 1:1 or 2:1 allowing users to enjoy cleaner drinking water more quickly and reliably.
How to reduce waste water in the RO system
Reverse Osmosis (RO) systems produce wastewater as part of their filtering process; passing water through a semipermeable membrane removes contaminants while flushing away waste water produced from this filtration step; however there are ways in which reverse Osmosis systems can minimize waste water production and waste water disposal costs.
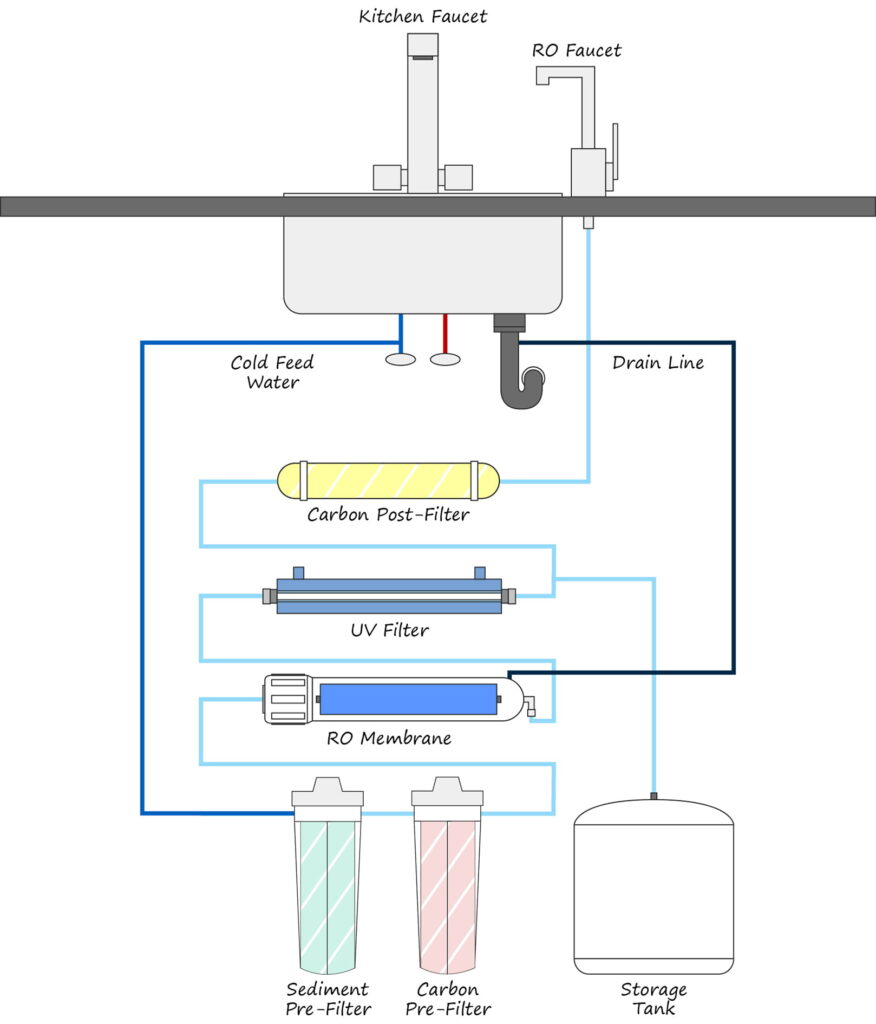
Image credit: best-osmosis-systems.com
Upgrade to a Modern RO System: Modern RO systems have been created with efficiency in mind, producing cleaner water with lower waste-to-clean ratios; in some cases these ratios reach 1:1!
Maintain Appropriate Water Pressure: Water pressure plays an integral part in filtering systems, with ideal levels between 35-40 PSI allowing water to pass efficiently through membranes without damage or degradation, increasing system efficiency.
Regular Maintenance and System Upgrades: Performing routine maintenance activities such as cleaning, component checks and filter replacement can significantly enhance efficiency of a wastewater system. Likewise, permeate pumps which reduce back pressure can save up to 85% of wastewater production while membrane upgrade kits add another RO membrane that further boost its performance and efficiency.
Repurpose Wastewater: Even with best efforts in place to minimise waste production, some wastewater remains. However, this water can still be put to good use; car washing, gardening, household cleaning, laundry pre-rinsing and toilet flushing among many other purposes may all use non-potable sources like this wastewater. It is crucial that its total dissolved solids (TDS) levels remain balanced to avoid using it for tasks like cooking and bathing.
Consider Systems That Recycle Water: Certain RO systems are specifically designed to recycle water and reduce wastewater output. Which purifier does not waste water? There are various models which prevent wastage; see references provided above for details.
Which water purifier does not waste water?
Several types of water purifiers minimise water wastage, as highlighted in the provided references.
KENT RO Water purifiers utilize proprietary Mineral RO Technology that combines Reverse Osmosis (RO) and Ultra Violet Filtration / Ultra Filtration (UF). KENT RO utilizes a computerized process which recovers over 50% of purified water while simultaneously storing rejected water separately for alternative uses – helping minimise wastage of resources.
Ultrafiltration: Ultrafiltration is an innovative filtration process which consistently yields no wastewater at low water pressure without needing energy/electricity or storage tanks for storage purposes.

Ultrafiltration (UF) is an efficient water purification technique that utilizes semipermeable membranes to filter out particulate matter, complex chemicals, heavy metals pollutants organic molecules viruses salts from water for purification purposes. Pore sizes in an UF membrane typically range between 0.001-0.1 microns which only permit particles smaller than 20nm to pass through; it has proven its worth as an effective technology solution against severe pollution issues in water bodies around the globe.
One of the primary advantages of ultrafiltration (UF) systems is their ability to function at low pressures without needing electric power; making UF an attractive choice across a range of sectors and industries including drinking water production, wastewater treatment and multiple industries such as dairy production, metal, textile, pharmaceutical and chemicals production and processing. Furthermore, this technique may serve as pretreatment prior to reverse osmosis systems as well as combined biological purification in membrane bioreactors.
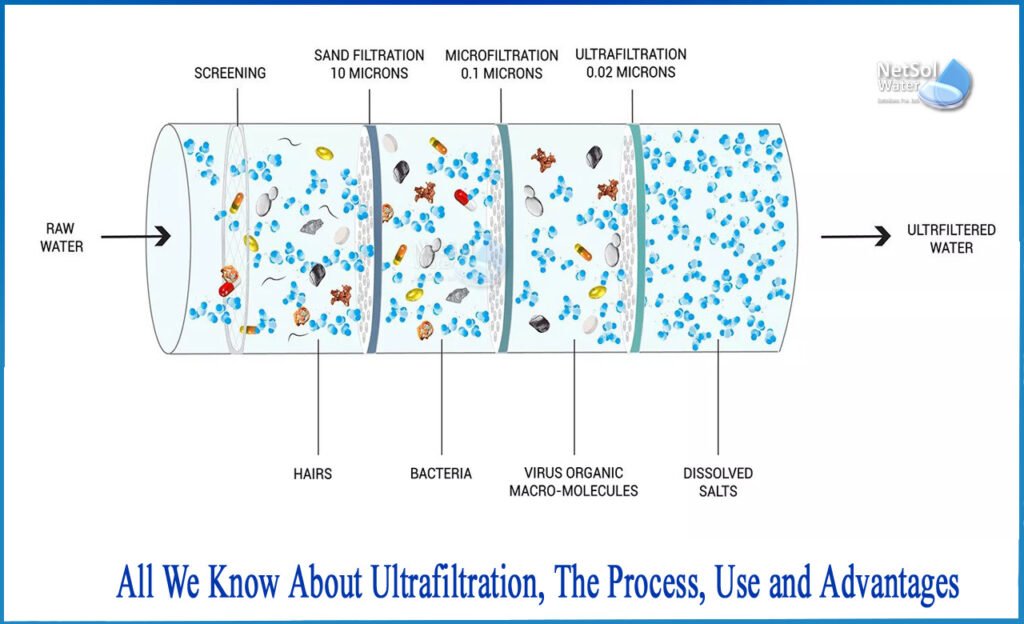
Image credit: netsolwater.com
While UF systems offer many advantages, they also come with limitations. One major drawback of using an UF process is particles accumulating on its membrane surface requiring regular maintenance cleaning to keep functioning optimally. Furthermore, this type of treatment cannot remove dissolved salts efficiently nor detect biological contaminants efficiently.
UF filter technology provides many advantages for water purification. While there may be limitations associated with it, such as operating at lower pressures or not needing electricity to operate effectively remove contaminants in various forms and contexts. Maintenance costs remain present but are easily offset by its ability to provide safe drinking water as well as versatility within industrial settings – therefore exploring UF plant options as cost-effective solutions should be seriously considered for safe drinking water and other water treatment requirements.
What Are Zero Waste RO Systems and How Do They Function in India? Zero Waste Reverse Osmosis systems (Zero Waste RO for short) in India represent an innovative technology designed to minimise water wastage when purifying drinking water, such as KENT and Permionics systems which ensure every drop that enters their purifiers are used efficiently rather than going down the drain unnecessarily.
Traditional RO systems waste an impressive volume of purified water during their purification processes, often discarding high TDS content water that’s often considered waste. But Zero Waste RO technology takes an innovative approach by redirecting this rejected water back to an overhead tank rather than leaving it for waste; an extra pump in the system pushes rejected water back through for reuse; eventually this recycled water becomes regular tap water ready for household uses such as washing and cleaning tasks.
What are Zero Waste RO systems, and how do they work?
Zero Waste RO (Reverse Osmosis) systems in India are an innovative technology that minimises water wastage during water purification. These systems, introduced by companies like KENT and Permionics, ensure that every drop of water into the purifier is optimally used and not wasted.
Traditional RO systems discard a substantial amount of water during the purification process. This rejects water, often high in total dissolved solids (TDS), and is usually considered waste. However, Zero Waste RO technology redirects this rejected water back to the overhead tank instead of allowing it to go to waste. This is achieved by an additional pump in the system that pushes the rejected water for reuse. The rejected water is diluted and repurposed as regular tap water for household use, such as washing and cleaning.
How much water does an RO system use?
The amount of water an RO system consumes and wastes depends heavily upon its efficiency; less efficient systems could utilize and produce four times as much purified water for each gallon of wastewater generated, while modern, more advanced ROs may boast improved ratios such as 1:2 or 2:1 which means two gallons of purified water produced for every one liter of wastewater generated.
To estimate annual wastewater production by your RO system, multiplying monthly drinking water usage times the wastewater percentage then by 12. This will give a rough idea of its annual production.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recognizes the issue of water wastage caused by RO systems. They have proposed draft specifications for WaterSense labelling of such RO systems in order to promote them as water efficient alternatives.
Though RO water purification processes waste considerable water, they remain highly effective, eliminating up to 99% of pollutants such as lead and asbestos from water supplies. Wastewater that contains beneficial minerals could be reused as watering plants; however due to high concentrations of dissolved solids it should never be used for cooking or bathing activities.
Also read,
Annual Maintenance Cost of RO Water Purifier
Sources:







